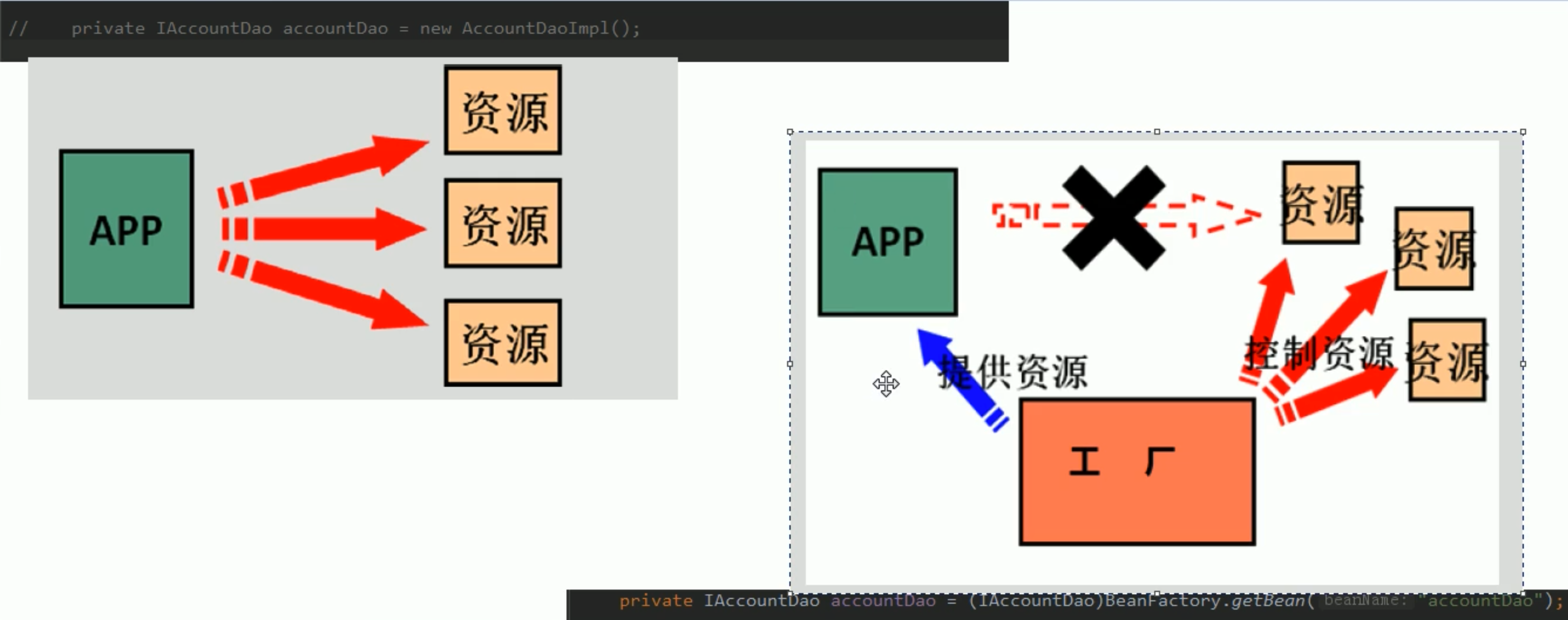
通常情况下类的调用和创建都是引入 然后直接通过new的方式来操作
但是这种操作的方式会让类之间的耦合度很高 不利于代码的维护
一般简单解耦操作可以通过以下方式:
-
创建配置文件,内部包含需要实例化的类名
-
通过工厂类 使用反射的方式创建类的实例
bean.properties
accountService=cn.leokim.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl accountDao=cn.leokim.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl
BeanFactory
public class beanFactory{
//定义一个properties对象
provate static Properties props;
//使用静态代码块为Properties对象赋值
static{
try{
props = new Properties();
//获取properties文件的流对象
inputStream in = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoder().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties");
porps.load(in);
}catch(Exception e){
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError("初始化props失败.");
}
}
//根据Bean的名称获取bean对象
public static Object getBean(String beanName){
Object bean = null;
try {
String beanPath = props.getProperty(beanName);
// System.out.println(beanPath);
bean = Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance();//每次都会调用默认构造函数创建对象
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
}
如果需要单例模式可以通过以下方法在static静态代码块里将类直接实例化好,在getBean的时候直接返回实例化好的类
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
public class BeanFactory {
//定义一个Properties对象
private static Properties props;
//定义一个Map,用于存放我们要创建的对象。我们把它称之为容器
private static Map<String,Object> beans;
//使用静态代码块为Properties对象赋值
static {
try {
//实例化对象
props = new Properties();
//获取properties文件的流对象
InputStream in = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties");
props.load(in);
//实例化容器
beans = new HashMap<String,Object>();
//取出配置文件中所有的Key
Enumeration keys = props.keys();
//遍历枚举
while (keys.hasMoreElements()){
//取出每个Key
String key = keys.nextElement().toString();
//根据key获取value
String beanPath = props.getProperty(key);
//反射创建对象
Object value = Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance();
//把key和value存入容器中
beans.put(key,value);
}
}catch(Exception e){
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError("初始化properties失败!");
}
}
/**
* 根据bean的名称获取对象
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
public static Object getBean(String beanName){
return beans.get(beanName);
}