一、什么是反射?
Java反射说的是在运行状态中,对于任何一个类,我们都能够知道这个类有哪些方法和属性。对于任何一个对象,我们都能够对它的方法和属性进行调用。我们把这种动态获取对象信息和调用对象方法的功能称之为反射机制。
二、反射的三种方式
这里需要跟大家说一下,所谓反射其实是获取类的字节码文件,也就是.class文件,那么我们就可以通过Class这个对象进行获取。
1、第一种方式
getClass
public final Class<?> getClass()
Returns the runtime class of this Object. The returned Class object is the object that is locked by static synchronized methods of the represented class.
返回类的运行实例
这个方法其实是Object的一个方法,Class继承了Object,所以我们可以直接使用。
package cn.leokim;
public class Reflact {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个对象
Test t = new Test();
//获取该对象的Class对象
Class c = t.getClass();
//获取类名称
System.out.println(c.getName());
}
}
2.第二种方式
package cn.leokim;
public class Reflact {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c = Test.class
//获取类名称
System.out.println(c.getName());
}
}
3.第三种方式
package cn.leokim;
public class Reflact {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这里需要注意,通过类的全路径名获取Class对象会抛出一个异常,如果根据类路径找不到这个类那么就会抛出这个异常。
try {
Class c = Class.forName("cn.leokim.Test");
//获取类名称
System.out.println(c.getName());
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
那么这3中方式我们一般选用哪种方式呢?第一种已经创建了对象,那么这个时候就不需要去进行反射了,显得有点多此一举。第二种需要导入类的包,依赖性太强。所以我们一般选中第三种方式。
三、通过反射获取类的构造方法、方法以及属性
1、获取构造方法
package cn.leokim;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class Reflact {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
//加载Class对象
Class c = Class.forName("cn.leokim.Test");
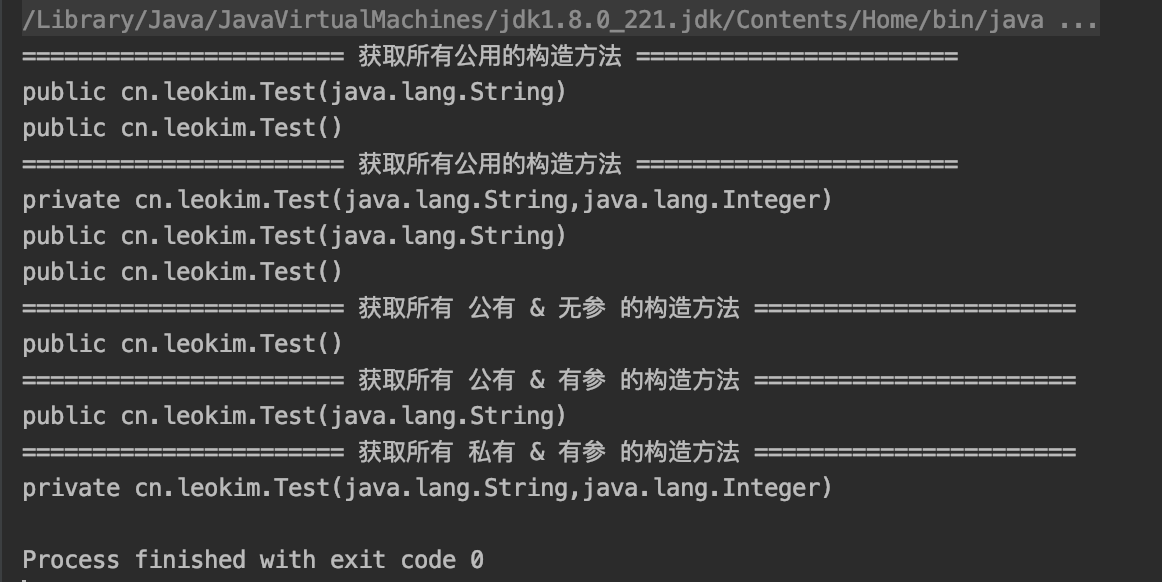
System.out.println("======================= 获取所有公用的构造方法 =======================");
//获取所有公用的构造方法
Constructor[] constructors = c.getConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors){
System.out.println(constructor);
}
System.out.println("======================= 获取所有公用的构造方法 =======================");
//获取所有构造方法
Constructor[] declareConsturctors = c.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor declareConsturctor : declareConsturctors){
System.out.println(declareConsturctor);
}
System.out.println("======================= 获取所有 公有 & 无参 的构造方法 =======================");
Constructor constructor = c.getConstructor(null);
System.out.println(constructor);
System.out.println("======================= 获取所有 公有 & 有参 的构造方法 =======================");
Constructor constructor1 = c.getConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(constructor1);
System.out.println("======================= 获取所有 私有 & 有参 的构造方法 =======================");
Constructor declareConsturctors1 = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, Integer.class);
System.out.println(declareConsturctors1);
}
}
结果:
2、获取类属性
Test.java
package cn.leokim;
public class Test {
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String name;
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
private String sex;
public String public_field2;
private String private_field3;
public Test() {
System.out.println("no args constructor");
}
public Test(String name){
System.out.println("Test: "+ name);
}
private Test(String name, Integer age){
System.out.println("Name: "+ name + "Age "+ age );
}
public void t(){
System.out.println("print t function.");
}
}
Reflact.java
package cn.leokim;
import sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.ObjectHeap;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Reflact {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//加载Class对象
Class c = Class.forName("cn.leokim.Test");
// System.out.println("======================= 获取所有公用的构造方法 =======================");
// //获取所有公用的构造方法
// Constructor[] constructors = c.getConstructors();
//
// for (Constructor constructor : constructors){
// System.out.println(constructor);
// }
//
// System.out.println("======================= 获取所有公用的构造方法 =======================");
// //获取所有构造方法
// Constructor[] declareConsturctors = c.getDeclaredConstructors();
//
// for (Constructor declareConsturctor : declareConsturctors){
// System.out.println(declareConsturctor);
// }
//
// System.out.println("======================= 获取所有 公有 & 无参 的构造方法 =======================");
// Constructor constructor = c.getConstructor(null);
// System.out.println(constructor);
//
// System.out.println("======================= 获取所有 公有 & 有参 的构造方法 =======================");
// Constructor constructor1 = c.getConstructor(String.class);
// System.out.println(constructor1);
//
// System.out.println("======================= 获取所有 私有 & 有参 的构造方法 =======================");
// Constructor declareConsturctors1 = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, Integer.class);
// System.out.println(declareConsturctors1);
System.out.println("========= 获取所有的公共字段 ==========");
Field[] fields = c.getFields();
for(Field field : fields){
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("========= 获取所有的字段(public & private) ==========");
Field[] declaredFields = c.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field : declaredFields){
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("========= 获取公有字段并使用 ==========");
Field field = c.getField("name");
Object obj = c.getConstructor().newInstance();
//为属性设置值
field.set(obj, "LeoKim");
Test test = (Test) obj;
System.out.println("Name is: " + test.getName());
System.out.println("========= 获取私有字段并使用 ==========");
Field field1 = c.getDeclaredField("sex");
Object obj1 = c.getConstructor().newInstance();
//暴力反射
field1.setAccessible(true);
field1.set(obj1, "男");
Test test1 = (Test) obj1;
System.out.println(test1.getSex());
}
}[object Object]
这里需要注意,在获取私有属性的时候如果没有进行暴力反射,那么会抛出下面这个异常。
3.获取类中的方法
先定义几个方法
public void method1(String str){
System.out.println("public method.");
}
private void method2(){
System.out.println("private method.");
}
String method3(String name, String sex){
System.out.println("default method: " + name + " & " + "sex");
return name + sex;
}
protected void method4(){
System.out.println("protected method.");
}
正题:
package cn.leokim;
import sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.ObjectHeap;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Reflact {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, InterruptedException {
//加载Class对象
Class c = Class.forName("cn.leokim.Test");
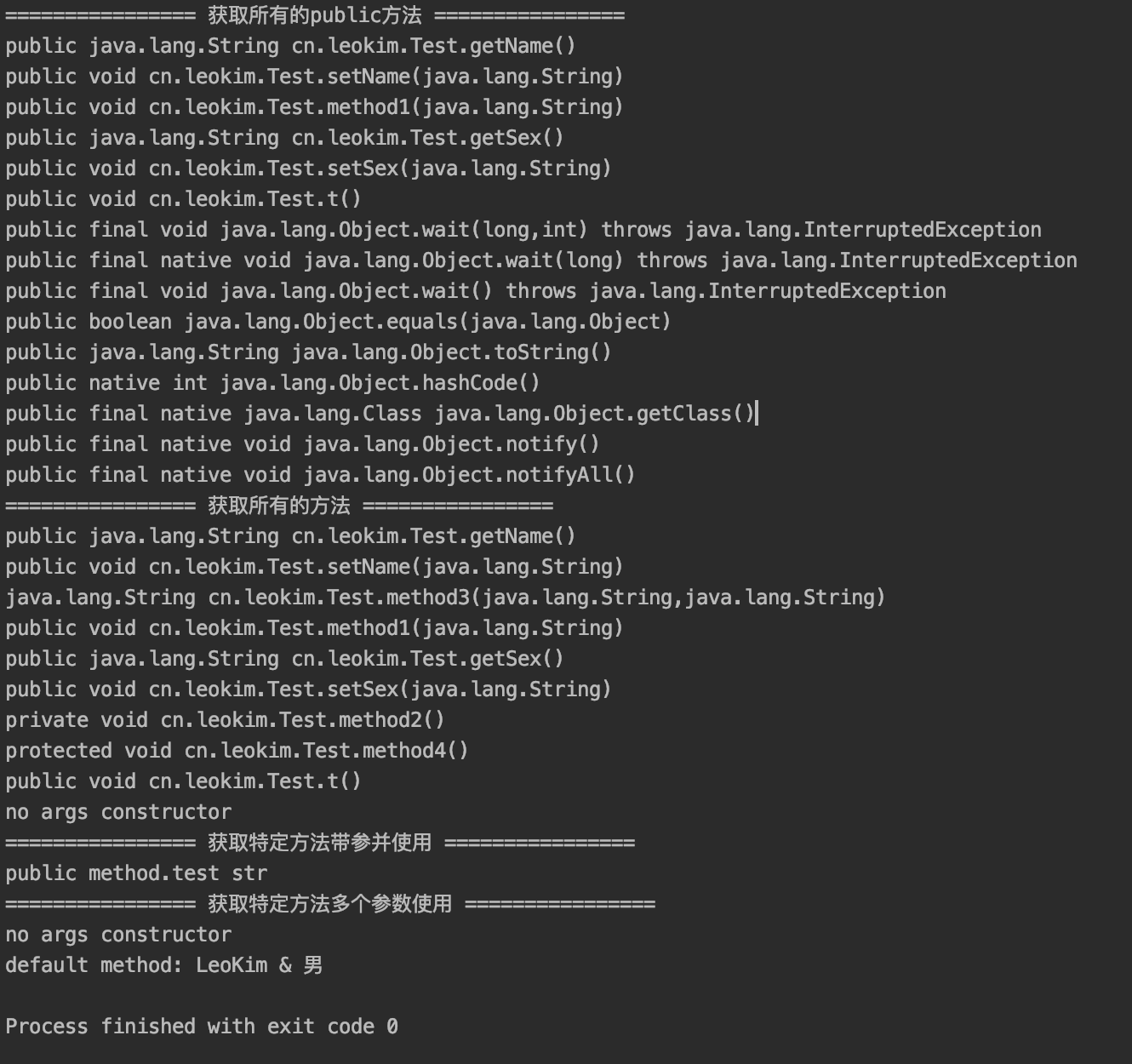
System.out.println("================ 获取所有的public方法 ================");
Method[] methods = c.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods){
System.out.println(method);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("================ 获取所有的方法 ================");
Method[] declaredMethods = c.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : declaredMethods){
System.out.println(method);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("================ 获取特定方法带参并使用 ================");
Method method1 = c.getMethod("method1", String.class);
Object obj1 = c.getConstructor().newInstance();
Test test1 = (Test) obj1;
test1.method1("test str");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("================ 获取特定方法多个参数使用 ================");
Method method3 = c.getDeclaredMethod("method3", String.class, String.class);
Object obj = c.getConstructor().newInstance();
//给方法传值
Object invoke = method3.invoke(obj, "LeoKim", "男");
System.out.println(invoke);
}
}
四、反射执行main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (String arg : args) {
System.out.println(arg);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Method method = Class.forName("cn.leokim.Test").getMethod("main", String[].class);
method.invoke(null, (Object)new String[]{"111", "222", "333"});
}